
An Indian village right on the India-Tibet LAC in Uttarakhand | India Sentinels

A more imminent threat presently comes from Nepal as a Chinese proxy. On May 8, 2020, an argument erupted between India and Nepal. The immediate reason which triggered the debate was an 80-kilometre road between Darchula and Lipulekh, the border pass near the trijunction with Tibet and Nepal. The road is to be used by Indian pilgrims visiting Kailash-Mansarovar located some 90 kilometres from the pass, as well as by local traders. Strategically, this road is also crucial for India. Although China does not have any claim in the area, it is clear that it has been inciting Nepal to claim Kalapani and beyond to destabilise India.
Introduction
What is known today as the ‘disputed’ Indian boundary with China (I generally call it the India-Tibet border), is usually divided into three sectors: Western, Central and Eastern. It is inaccurate not to add the Gilgit-Baltistan Sector, presently occupied by Pakistan and partly by China as the Shaksgam Valley but the latteris not within the purview of this article.
During the last four years, India’s Western and Eastern Sectors have witnessed a number of intrusions, and in some cases, confrontations, between the Indian Army and China’s People’s Liberation Army (PLA). Such incidents have occurred since May 2020 in EasternLadakh and, for instance, in the Yangtse sector of Arunachal Pradesh in December 2022. The Central Sector has been relatively quieter, but remains vital for the defence of the nation.
The confrontation in Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh (where Beijing has renamed villages for the fourth time since 2017) will not end soon.It is therefore time to ask if there is a possibility that the PLA will open another front in the Central Sector of the northern boundary.
Central Sector
In 1960, during the course of negotiations with China, Indian officials defined the sector thus: “From the Gya Peak the boundary follows the watershed between the Spiti and Pare rivers and crosses the Pare river a mile south of the village of Kaurik. South of the Pare river the boundary ascends one of the ranges leading to the high peak of Leo Pargial, crosses the Sutlej at its bend, and following the Zaskar range lies through the Shipki Pass, the Raniso Pass, and the Shimdang Pass. Thereafter, it follows the main watershed between the Sutlej and the Ganges basins. Passes such as Tsangchok-la, Mana-la, Niti-la, Tunjun-la, Kungri Bingri-la, Darma-la mark the boundary.”
The sector ends at the tri-junction between India, Nepal and Tibet, located near Tinkar Lipu (pass), South of Lipilekh-la. The Central Sector is the area of responsibility of the Central Command of the Indian Army, headquartered in Lucknow.
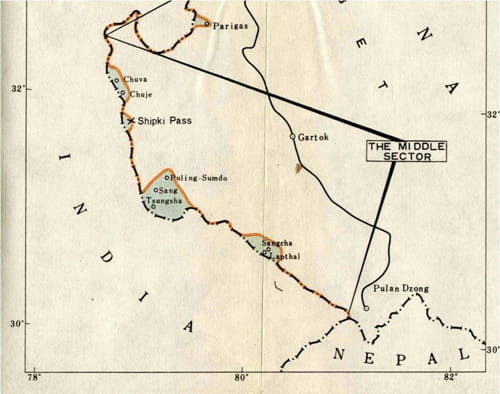
Theoretically, there should be no dispute in this sector as the boundary follows the main watershed.However, China still claims six places within Indian territory.
China’s ‘Historical Claims’
Chinese Claims in a Letter from Zhou Enlai, December 1962
It is worth looking at the ‘historical’ claims made by Beijing in the Central Sector. On November 20, 1950, during a question and answer session in Parliament, Prime Minister Nehru was asked: “Will the Prime Minister be pleased to state whether India has got any well-defined boundary with Tibet?”
His answer was: “The border from Ladakh to Nepal has probably not been the subject of any formal agreement between India, Tibet and China but it is well established by custom and long usage. The Historical Division is investigating if there are any formal agreements. There have been a few boundary disputes in this area but they have been peacefully settled.” It is a historical fact that the India-Tibet frontier was peaceful.
However, in June 1954, a couple of months after signing the Tibet (Panchsheel) Agreement, China made incursions atBarahoti. In the following months and years, intrusions and confrontations were noted in Shipkila, Damzam (Niti), Nilang among others, all in the Central Sector.
Facsimile of the 1954-1959 White Paper 1
For Beijing, there are six ‘disputed’ areas in the Central Sector which stretch over the states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand; namely Chuva-Chuje, near Sumdo/Kaurik in Kinnaur district, an area south of Shipki-la (pass) in the same district; Nilang-Jadhang in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand; and three areas in Chamoli district, namely Barahoti, Lapthal and Sangchamalla; to this one should add Kalapani/Lipulekh, recently includedin Nepal’s new maps.
A Note from the Historical Division
On July 30, 1980, the Historical Division of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) sent a secret note to the East Asia (EA) Division, dealing with China:the EA Division wanted to know if there was any Chinese claim in the Central Sector.
The note described the area thus: “This sector of the boundary has natural features of watersheds, mountain passes and river valleys.” These geographical features marked the border.
It was explained that during the 1960 talks with China, Indian officials brought forward conclusive evidence: “to show that the alignment had throughout its length a traditional and customary basis reaching back through many centuries.”
On November 14, 1962, while the border war with China was raging, in a letter to Zhou Enlai, Nehru told his counterpart: “The Chinese government has never had any authority south of the main Himalayan watershed ridge, which is the traditional boundary in this sector.” This did not stop Beijing from claiming six areas in the sector.
The ‘Disputed’ Places
Barahoti
As mentioned earlier, in 1954, the earliest Chinese incursion occurred here, making it the first‘ disputed’ place in the entire boundary.
In 1958, as an unnecessary compromise, Delhi agreed to both sides withdrawing their armed personnel from the locality, “[even though] Indian civilian personnel have throughout been functioning [there].” Since then, every summer, the Chinese regularly visit Barahoti.
One issue is that the Chinese claims are not uniformly based on the principles normally used to demarcate a boundary: that includes, watershed, river, customary routes, grazing rights, among others.
When exchange of maps took place in 2000 for the Central Sector, Barahoti was the only place still claimed by China within their Line of Actual Control. One can only say that the Chinese claim to the area is far-fetched, as it clearly lies south of the watershed (Tunjun-la). But as Beijing promotes first and foremost its own interests and refuses to follow universally recognised conventions, it is difficult to envisage a quick solution; India should hence be ready to deal with trouble in these ‘dormant’ Chinese claimed areas in the Central Sector.
Chuva-Chuje
Another ‘disputed’ area is ‘Chuva-Chuje’ in Kinnaur district of Himachal Pradesh. Though the Chinese have not recently insisted on the return of this remote place, it has been reported that the populations of the Lahaul,Spiti, and Kinnaur districts are becoming increasingly nervous; they expressed serious concerns as China has been building Xiaokang (moderately well-off) border villages as well as roads leading to the Indian border. Though dormant since the end of the 1950s, Chuva and Chuje have been on China’s claim-list to extend its territory.
The case of Shipki la
This is another tenuous claim from China, with no historical, cartographical or geographical backup. Presently, it is a dormant claim, but with Beijing in the mood to claim Vladivostok (and parts of Ladakh), it is worth looking into the facts.
On September 1, 1956, Delhi received a report that a party of about 10 Chinese Army personnel entered and took up position about 2 furlongs from Hupsong Khad on the Indian side of Shipki-la Pass. Later, the Chinese withdrew after an officer of the Indian Border Police informed the Chinese that the Indian territory extended up to the Shipki-la. But the matter continued to be discussed during the following years.
Nilang, Jadhang and Pulamsumda
This ‘dispute’ is different from the two preceding cases, in that the area south ofTsangchok-la was disputed by the Tibetan government before India’s Independence. But it was a ‘gentle’ dispute between neighbours sharing the same values.
For the Tibetans, their claim was based on the fact that the Thirteenth Dalai Lama would have said that the border was located at a bridge on the Gumgum Nala on the way to Gangotri.
For the British, the principle of the watershed was the prime deciding factor and therefore Tsangchok-la was the border (since independence India has followed this principle).
Soon after the Chinese occupied Tibet in 1950/51, the situation which had been pending for decades, suddenly became pressing and Delhi had no other option but to send police patrols and take control of the place in 1952.
Lapthal and Sangchamalla
These two places are clearly south of the watershed and were added to itsclaims at a later stage by China.
A Recent Visit

Adi Kailash, Indo-Tibet boundary
A recent visit to the border areas in the Uttarkashi and Pithoragarh districts was aneye-opener. We first realised the considerable efforts made by the Central Government (through the Border Roads Organization under India’s Ministry of Defence) to connect the most remote villages and the furthestborder posts to the rest of the country.
A few years ago it took up to a 25 to 27 day-walk for a Kailash yatri to travel from Tawagath, 18 kilometres north of Darchula to Lipulekh and later come back (in Tibet, they were taken by buses to the Kailash basecamp). Today, the road reaches a few hundred metres from the top of Lipulekh, the border pass separating Kumaon (near the trijunction with Tibet and Nepal) from Purang County (Dzong) in Tibet.
The implication of this development is that the access to these areas for the Indian Army and the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) is far easier. Today, the defence forces can answer any contingency in the shortest possible time; it also makes the lives of the local population simpler.
The Dispute with Nepal
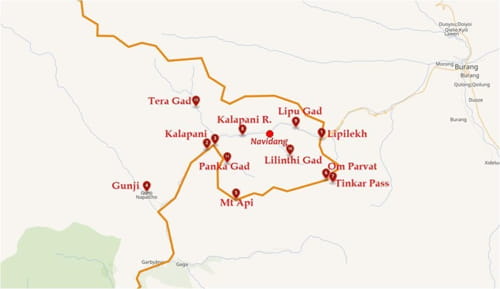
Kalapani area as per a Wikipedia map
A more imminent threat presently comes from Nepal as a Chinese proxy.
On May 8, 2020, an argument erupted between India and Nepal. The immediate reason which triggered the debate was an 80 km road between Darchula and Lipulekh, the border pass near the trijunction with Tibet and Nepal. The road is to be used by Indian pilgrims visiting Kailash-Mansarovar located some 90 kilometres from the pass, as well as by local traders.Strategically, this road is also crucial for India.
Although China does not have any claim in the area, it is clear that ithasbeen inciting Nepal to claim Kalapani and beyond to destabilise India.
Wang Junzheng, the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) Communist Party of China secretary, set the ball rolling during his visit to Kathmandu in November 2023.The Tibet delegation (without any Tibetans) announced that they wanted to maintain the “good momentum of high-level exchanges between two countries”.
A five-year initiative for Nepal’s northern border districts has been set-up, offering different kinds of logistical and material support, mostly for building schools and health posts and installingsolar electricity in Nepal’s15 northern districts. This means a more important Chinese presence in Nepal, including in the Darchula district of Nepal bordering India.
This comes at a time of recrudescence of the Nepali border claims in the Kalapani area, a worrying trend which should be closely monitored by New Delhi.
India should also not ignore some recent maps of the Indian boundary published in China. Though Beijing’s and New Delhi’s stands are similar in the Lipulekh/Kalapani sector, the Nepali claims are shown as ‘disputed’ by some ‘private’ maps in China. Knowing that there is nothing such as ‘private’ in China, it should not be ignored.
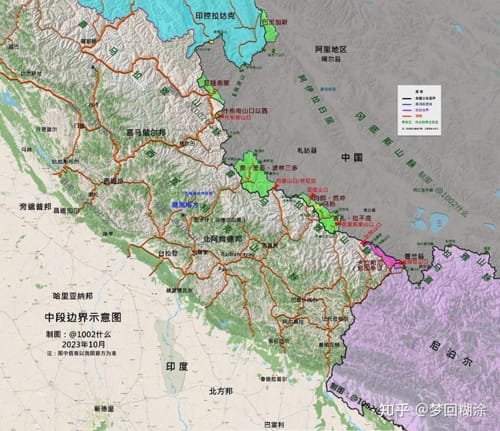
Chinese claims in the Central Sector, October 2023 | Chinese social media
(Exclusive to NatStrat)